Lipophilic composition of Scabiosa stellata L.: an underexploited plant from Batna (Algeria)Naima Rahmouni, Diana C. G. A. Pinto, Sónia A. O. Santos, Noureddine Beghidja, and Artur M. S. Silva Université des Frères Mentouri Constantine 1, Constantine, Algeria
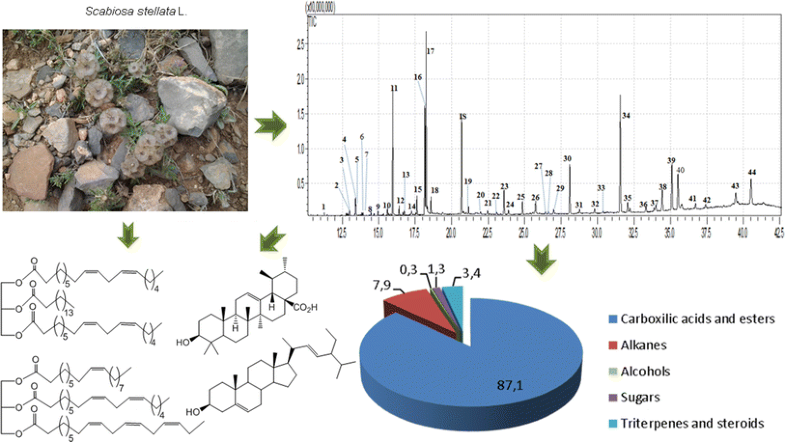
E-mail: artur.silva@ua.pt Abstract: Scabiosa stellata L. is the less-studied plant of the species belonging to the genus Scabiosa, but the fact that several Scabiosa species are used in traditional medicine is an incentive to study this species. The profile of the S. stellata hexane extract was established by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and allowed to conclude that fatty acids and their derivatives (87%) are the major chemical families of this extract. From the identified components, linoleic (19%), palmitic (20%) and linolenic (34%) acids are the major ones. Additionally, triterpenoids, namely β-sitosterol, stigmasterol, oleanolic and ursolic acids were also found. Simultaneously, the phytochemical study of this extract allowed the isolation and full characterization using 1D and 2D NMR experiments (1H and 13C NMR, HSQC, COSY, HMBC) of interesting metabolites such as 1,3-O-dilinoleoyl-2-O-palmitoyl glycerol and 1-O-linolenoyl-2-O-linoleoyl-3-O-oleoyl glycerol. This first assessment of S. stellata less polar constituents allowed the identification of several important compounds among which, ursolic and stearic acids, 1,3-O-dilinoleoyl-2-O-palmitoyl glycerol and 1-O-linolenoyl-2-O-linoleoyl-3-O-oleoyl glycerol, were found, for the first time in Scabiosa genus. The results reported, index of atherogenicity (AI = 0.55), index of thrombogenicity (TI = 0.23) and the fatty acid ratio (ω-6/ω-3 = 0.55), point out the nutritional value of S. stellata.
Keywords: Scabiosa stellata L. ; GC–MS profile ; Fatty acids ; Sterols ; Terpenes ; Nutritional indexes Full paper is available at www.springerlink.com. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-017-0308-3
Chemical Papers 72 (3) 753–762 (2018) |
Sunday, November 24, 2024 |
|||
© 2024 Chemical Papers |
||||