Synthesis, molecular docking, and evaluation of novel bivalent pyrazolinyl-1,2,3-triazoles as potential VEGFR TK inhibitors and anti-cancer agentsAhmed A. Abd-Rabou, Bakr F. Abdel-Wahab, and Mohamed S. Bekheit National Research Centre, Dokki, Giza, Egypt
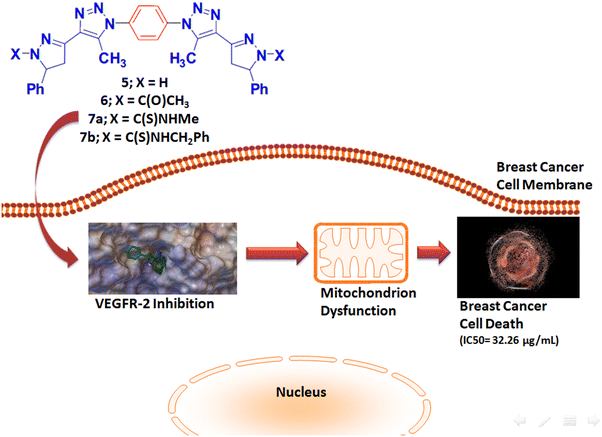
E-mail: bakrfatehy@yahoo.com Abstract: Investigations in the discovery of tyrosinase enzyme inhibitors have the potential to design novel anti-cancer drugs. A variety of novel bivalent pyrazolinyl triazoles 5–7 were synthesized and identified. The bis-acetyl triazole 3 was accomplished via two-step process first by preparation of diazide 2 followed its coupling reaction with acetylacetone in basic medium. The Claisen–Schmidt condensation reaction of 3 with two moles equivalent of benzaldehyde produces the corresponding bis-α, β-unsaturated ketone 4. Treatment of Schiff base 4 with excess hydrazine hydrate in either acetic acid or ethanol/DMF afforded the bis-N-acetylpyrazline 5 or bis-pyrazoline 6, respectively. Finally, treatment of 6 with two derivatives of isothiocyanate analog gives the bis-N-thioamide pyrazolines 7a and 7b. The synthesized compounds were evaluated as anti-tumor candidates against three human cancer cell lines (MCF-7, HepG2, and HCT-116). The bioscreening evaluation showed that compounds 7a and 6 had a significant antineoplastic potencies (IC50: 32.26 and 57.06 µg/mL) against breast MCF-7 and hepatic HepG2 cancerous cell lines, respectively, in relative to the standard drug, 5-fluorouracil. Molecular docking studies of the synthesized compounds were investigated as VEGFR2 TK inhibitors. Keywords: Bivalent ligands ; Pyrazoline ; Triazole ; VEGFR2 ; Computer-assisted molecular model ; Anti-cancer activity Full paper is available at www.springerlink.com. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-018-0451-5
Chemical Papers 72 (9) 2225–2237 (2018) |
Monday, May 19, 2025 |
|||
© 2025 Chemical Papers |
||||