Synthesis of novel indole derivatives containing double 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety as efficient bactericides against phytopathogenic bacterium Xanthomonas oryzaeKun Tian, Xiao-Qin Li, Li Zhang, Yi-Yuan Gan, Jiao Meng, Shou-Qun Wu, Jin-Lin Wan, Yang Xu, Chao-Ting Cai, Gui-Ping Ouyang, and Zhen-Chao Wang Guizhou University, Guiyang, People’s Republic of China
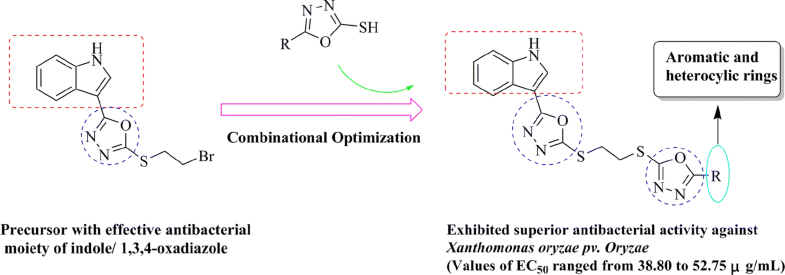
E-mail: oygp710@163.com Abstract: A series of novel indole derivatives containing double 1,3,4-oxadiazole moiety was designed, synthesized and evaluated for their antibacterial activities in vitro. These compounds were fully characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and HRMS. Bioassay results indicated that most of title compounds exhibited excellent antibacterial activities against rice bacterial pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae (Xoo). For example, compounds 7d, 7h, 7i, 7j, 7k, 7l and 7m had the half-maximal effective concentration (EC50) values of 52.31, 54.12, 40.65, 38.80, 51.13, 52.75 and 50.66 µg/mL, respectively, which was better than that of commercial product bismerthiazol (BMT) (85.18 µg/mL). The experimental results proved that indole derivatives bearing double 1,3,4-oxadiazole unit are promising candidates for the development of new agricultural bactericides against pathogenic bacterium Xoo. Keywords: Indole ; 1,3,4-Oxadiazole ; Antibacterial activity Full paper is available at www.springerlink.com. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-018-0555-y
Chemical Papers 73 (1) 17–25 (2019) |
Monday, May 19, 2025 |
|||
© 2025 Chemical Papers |
||||