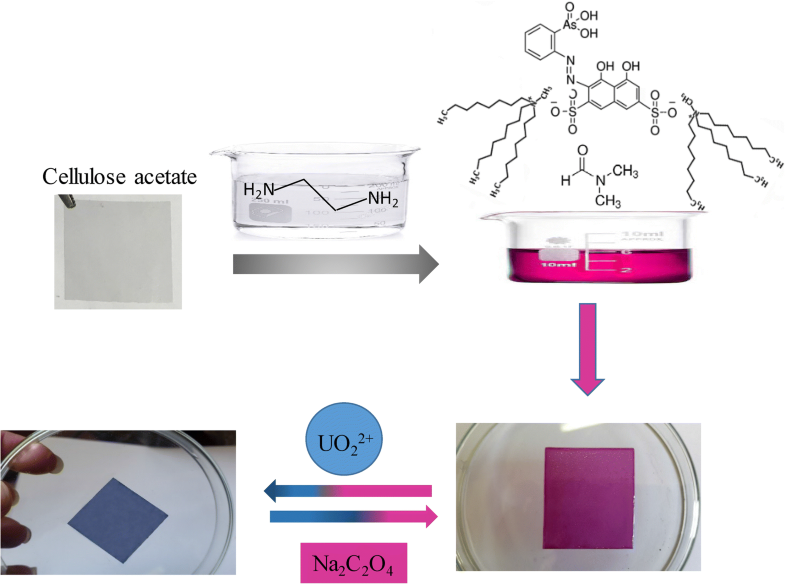
A portable sensor for environmental monitoring of uranium(VI): design, development and implementationMaryam Masoomi, Vida Rezaei, and Behzad Aibaghi Damghan University, Damghan, Iran
E-mail: v.rezaei@du.ac.ir Abstract: A novel and reversible optical sensor based on immobilization of 2,2′-(1,8-dihydroxy-3,6-disulfonaphthalene-2,7-bisazo) bisbenzenearsonic acid [arsenazo(III)] on a porous cellulosic polymer film as solid membrane support was developed and its application was considered in the determination of uranium(VI) in aqueous solutions. The procedure of immobilizing arsenazo on the membrane is useful for the fabrication of sensors using dye molecules that are unstable in ethylenediamine alkaline solution as the main solvent in preparation of optical sensors. The calibration curve was linear in the range of 0.01–4.00 μg mL−1 (3.70 × 10−8–1.48 × 10−5 mol L−1) of uranium in the sample solution, with a regression coefficient (r) of 0.9995. The detection limit (SNR = 3) was 0.006 μg mL−1 (2.20 × 10−8 mol L−1) and precision experiments resulted in good RSDs for both intra-day and inter-day precision. The proposed optical sensor can be successfully applied in the evaluation of this metal in different environmental water samples with satisfactory results. Keywords: Uranium(VI) optical sensor ; Arsenazo ; Porous cellulosic polymer ; Spectrophotometry Full paper is available at www.springerlink.com. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-019-00746-5
Chemical Papers 73 (8) 1961–1969 (2019) |
Thursday, April 03, 2025 |
|||
© 2025 Chemical Papers |
||||