Potential of Venlafaxine in the inhibition of mild steel corrosion in HCl: insights from experimental and computational studiesSumayah Bashir, Hassane Lgaz, III-Min Chung, and Ashish Kumar Lovely Professional University, Phagwara, India
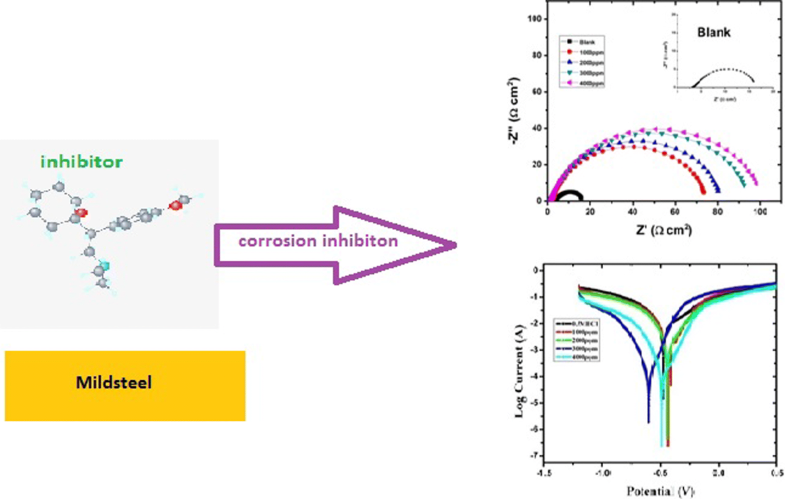
E-mail: drashishchemlpu@gmail.com Abstract: The corrosion-inhibiting behavior and adsorption of Venlafaxine on mild steel has been examined using 1 M HCl at 298 K. Techniques used include weight loss studies, potentiodynamic polarization studies, electron impedance spectroscopy, computational studies (Monte Carlo simulation studies) and AFM studies. The polarization data revealed that Venlafaxine mostly behaves as mixed type of inhibitor. The data from weight loss results suggested that inhibition efficiency varied directly with concentration and inversely with temperature. A quantum chemical calculation and molecular dynamic (MD) simulation studies were used to further validate inhibition mechanism. Keywords: Mild steel ; Weight loss ; Tafel ; DFT ; EIS Full paper is available at www.springerlink.com. DOI: 10.1007/s11696-019-00775-0
Chemical Papers 73 (9) 2255–2264 (2019) |
Monday, May 19, 2025 |
|||
© 2025 Chemical Papers |
||||